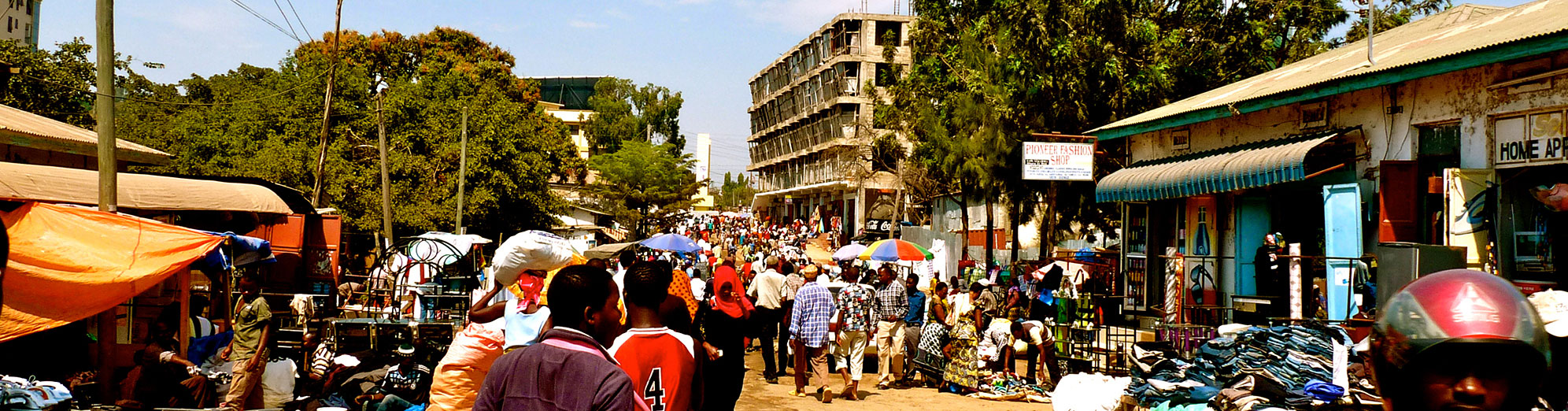
Urban Africa - Urban Africans: New encounters of the rural and the urban
At 3.5% Africa has the highest urbanization rate in the whole world. The potential effects of these staggering growth rates are relevant for all Africans, both in the urban as well as in the rural areas. By 2040 the continent’s cities are expected to have to accommodate 79 Million additional inhabitants. Between 2040 and 2050 the figure will rise to a staggering 84 Million. The latest UN-Habitat report forecasts that by 2025 Africa’s urban population will outstrip that of Europe and Latin America together. No wonder that a growing number of researchers, institutions and governments are paying more and more attention to urbanization in Africa. This growing interest focuses on whether rapid urbanization will overwhelm African governments and societies or whether it reflects the increasing importance of the middle classes, a factor which is held by many to account for Africa’s positive economic performance of late.
African urbanization trends raise several issues that are of interest to scholars. These range from politics (what does the growing importance of city dwellers mean to the character of politics?), through economics (will urbanization undermine or foster efforts at overcoming inequalities?), all the way to social (e.g. are African social relations changing in any significant way as a result of these trends? How do Africans live their cities?) and cultural issues (e.g. will urban life styles dominate the rural? How will the rural and the urban relate to each other in the future?).
The key issue, however, is how urbanization processes in Africa transform conventional objects of African Studies and how do scholars of Africa gear up to face such changes? This is the question which the Centre for African Studies at the University of Basel (CASB) in Switzerland wishes to invite scholars of Africa to engage with in a more conscious and systematic manner. While the urban will be prominent, the proposed conference theme will also look into the entanglements of the rural with the urban, especially with a view to addressing an implicit assumption underlying the study of Africa and which concerns the supposed rural ‘nature’ of the continent as well as the constitutive nature of the tension between tradition and modernity.
While over the past few decades a self-critical attitude within many disciplines has led to a weakening of these assumptions, the urban continues arguably to be seen as the exception or, at any rate, as analytically less consequential than the rural. ECAS 2017 “Urban Africa – Urban Africans” will, therefore, be an occasion for rethinking African Studies, but also for exploring and deepening research avenues that many researchers working on urban and rural issues have taken up over recent years. There is a critical mass to be harnessed in the effort to push the frontiers of critical European knowledge production on Africa.